unicornscan說明
針對 訊息收集 及網路分析
例如:
設定UDP網路掃描, IP:192.168.8.200
unicornscan -m U -Iv 192.168.8.200 :1-65535
例如:
設定UDP網路掃描, IP:192.168.8.200
unicornscan -m U -Iv 192.168.8.200 :1-65535
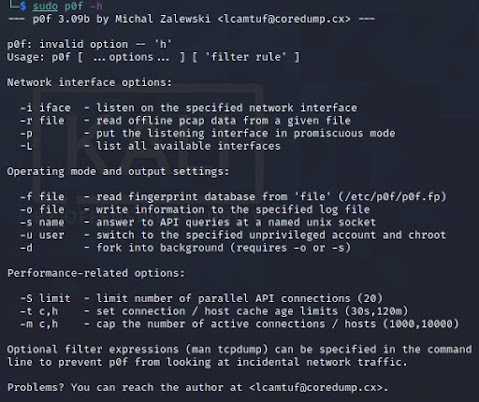
首先要先安裝: apt-get install unicornscan 看一下help : unicornscan -h
unicornscan (version 0.4.7)
usage: unicornscan [options `b:B:cd:De:EFG:hHi:Ij:l:L:m:M:o:p:P:q:Qr:R:s:St:T:u:Uw:W:vVzZ:' ] X.X.X.X/YY:S-E
-b, --broken-crc *set broken crc sums on [T]ransport layer, [N]etwork layer, or both[TN]
-B, --source-port *set source port? or whatever the scan module expects as a number
-c, --proc-duplicates process duplicate replies
-d, --delay-type *set delay type (numeric value, valid options are `1:tsc 2:gtod 3:sleep')
-D, --no-defpayload no default Payload, only probe known protocols
-e, --enable-module *enable modules listed as arguments (output and report currently)
-E, --proc-errors for processing `non-open' responses (icmp errors, tcp rsts...)
-F, --try-frags
-G, --payload-group *payload group (numeric) for tcp/udp type payload selection (default all)
-h, --help help
-H, --do-dns resolve hostnames during the reporting phase
-i, --interface *interface name, like eth0 or fxp1, not normally required
-I, --immediate immediate mode, display things as we find them
-j, --ignore-seq *ignore `A'll, 'R'eset sequence numbers for tcp header validation
-l, --logfile *write to this file not my terminal
-L, --packet-timeout *wait this long for packets to come back (default 7 secs)
-m, --mode *scan mode, tcp (syn) scan is default, U for udp T for tcp `sf' for tcp connect scan and A for arp
for -mT you can also specify tcp flags following the T like -mTsFpU for example
that would send tcp syn packets with (NO Syn|FIN|NO Push|URG)
-M, --module-dir *directory modules are found at (defaults to /usr/lib/unicornscan/modules)
-o, --format *format of what to display for replies, see man page for format specification
-p, --ports global ports to scan, if not specified in target options
-P, --pcap-filter *extra pcap filter string for reciever
-q, --covertness *covertness value from 0 to 255
-Q, --quiet dont use output to screen, its going somewhere else (a database say...)
-r, --pps *packets per second (total, not per host, and as you go higher it gets less accurate)
-R, --repeats *repeat packet scan N times
-s, --source-addr *source address for packets `r' for random
-S, --no-shuffle do not shuffle ports
-t, --ip-ttl *set TTL on sent packets as in 62 or 6-16 or r64-128
-T, --ip-tos *set TOS on sent packets
-u, --debug *debug mask
-U, --no-openclosed dont say open or closed
-w, --safefile *write pcap file of recieved packets
-W, --fingerprint *OS fingerprint 0=cisco(def) 1=openbsd 2=WindowsXP 3=p0fsendsyn 4=FreeBSD 5=nmap
6=linux 7:strangetcp
-v, --verbose verbose (each time more verbose so -vvvvv is really verbose)
-V, --version display version
-z, --sniff sniff alike
-Z, --drone-str *drone String
*: options with `*' require an argument following them
address ranges are cidr like 1.2.3.4/8 for all of 1.?.?.?
if you omit the cidr mask then /32 is implied
port ranges are like 1-4096 with 53 only scanning one port, a for all 65k and p for 1-1024
example: unicornscan -i eth1 -Ir 160 -E 192.168.1.0/24:1-4000 gateway:a



留言
張貼留言